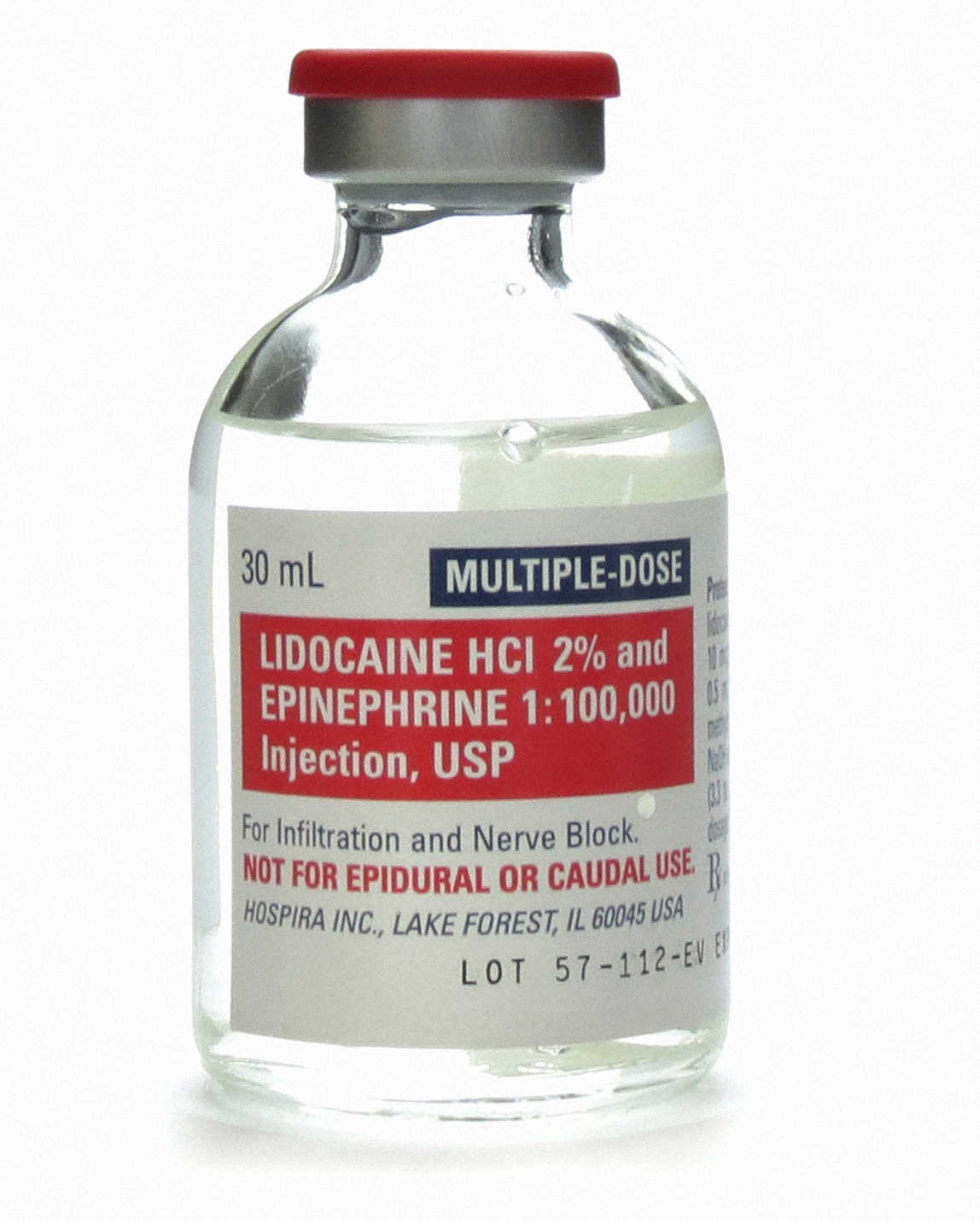
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia.
The efficacy profile of lidocaine as a local anaesthetic is characterized by a rapid onset of action and intermediate duration of efficacy. Therefore, lidocaine is suitable for infiltration, block, and surface anaesthesia. Longer acting substances such as bupivacaine are sometimes given preference for spinal and epidural anaesthesias.
It is one of the most commonly used local anaesthetics in dentistry. It can be administered in multiple ways, most often as a nerve block or infiltration, depending on the type of treatment carried out and the area of the mouth worked on.
As of 2021, lidocaine is not listed by the World Anti Doping Agency as a substance whose use is banned in sport.