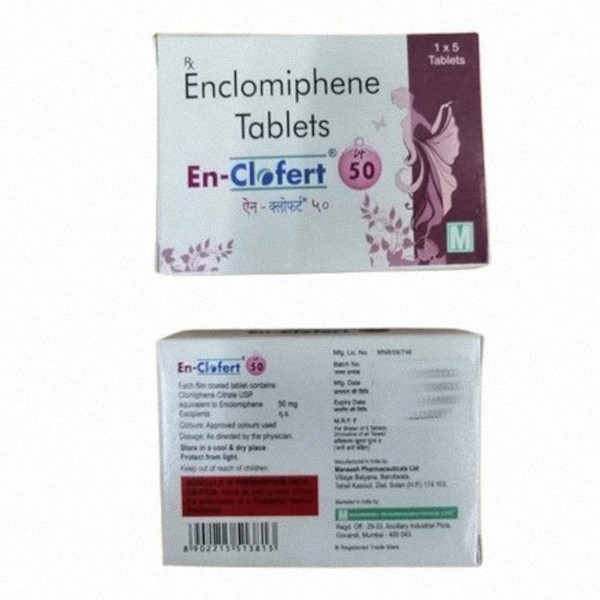
Enclomifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator of the triphenylethylene group and acts by antagonizing the estrogen receptor (ER) in the pituitary gland, which reduces negative feedback by estrogen on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thereby increasing gonadotropin secretion and hence gonadal production of testosterone.
It is primarily used as a treatment for men with persistent low testosterone as a result of secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. In secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, the resulting low levels of testosterone is attributed to inadequacies in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. In contrast, primary hypogonadism is caused by defects in the testes that causes them to be unable to produce the required amount of testosterone.
Enclomiphene, which stimulates the endogenous production of testosterone, is not currently known to have common adverse effects of exogenous testosterone replacement therapy, such as reduced spermatogenesis or infertility.
In addition, research has uncovered that enclomiphene increases total and free testosterone levels without increasing dihydrotestosterone disproportionately, suggesting that it “normalizes endogenous testosterone production pathways and restores normal testosterone levels in men with secondary hypogonadism.”